
Rivers in India
Posted By MariaA number of freshwater sources occupy the Indian region. The country’s population relies heavily on the rivers in India for water, a means of economical transport, fishing as well as the generation of hydroelectric power. These rivers provide a means of earning to a large number of Indians. On the other hand, most of these waterways are also considered sacred to the Hindus and have a special place in their religion.
Discussed below are the major rivers which flow through India and enrich the country with fertility and precious resources like freshwater and food.
Ganges River
Also known as Ganga by the Indians, the Ganges River emerges from the Himalayan Ranges in Uttarakhand state. In terms of the volume of water, it is the biggest river system in the entire Indian subcontinent. The river flows to a length of 2,510 kilometers and forms the Ganges River System when ten of its major tributaries join it. The river also passes through Bangladesh during its course and completes its journey at the Bay of Bengal into which it empties its waters to join the Indian Ocean.

Go through the following interesting facts about the Ganges River.
- The river’s drainage area occupies 1,000,000 square kilometers. The land is very fertile and has been helping the country immensely in its agricultural sector.
- The Ganges River System provides water to both India as well as Bangladesh all the year round.
- The river is associated with the Ganga goddess and is deemed sacred by the Hindus. According to the religion, bathing in the water of the Ganges purifies individuals from their previously committed sins.
- More than a hundred fish species and over fifty different varieties of amphibians are found in the waters of the river.
- The river might purify one spiritually according to the belief of Hindus, but it actually contains a high level of domestic and industrial waste. It is not only unfit for drinking by humans but also harms the organisms found in the river.
- Two endangered species which once flourished in the waters of Ganga are the Ganges Shark and Ganges River Dolphin.
- The Ganges basin is home to the largest population found in any river basin of the world. It is estimated to be around four hundred million.
- The fertile soils of the basin are irrigated by the river for important crops like wheat, sugarcane and rice.
Godavari River
The second longest of the rivers in India, Godavari begins its journey from the state of Maharashtra and continues up to the Bay of Bengal. During this course, it flows for 1,465 kilometers discharging an average of 3,505 cubic meters per second. In addition, one of the country’s largest river basins is formed by Godavari, covering a huge area of 312,812 square kilometers.

Have a look at the following interesting information about the Godavari River.
- The river holds religious importance for the Hindus of the country. Several Hindus as well as Sikh temples are located at the river’s banks where devotees perform pilgrimage.
- The river is often referred to as the Ganga of the South owing to its religious significance.
- Pushkaram is an important bathing festival which is held after a period of every 12 years at the banks of the sacred River.
- The growth of industrialization as well as urbanization has polluted the waters of the Godavari River.
- Emerging from District Nasik in Maharashtra, the river flows through four other states of the country while its drainage basin consists of six states.
Krishna River
Ranking third among the longest rivers in India, the Krishna River flows for a length of 1,300 kilometers. Its source lies in the Maharashtra state while its final destination is the Bay of Bengal. The basin area of the river is significant due to its fertility and houses a large population of the country. It covers an area of 258,948 square kilometers.

More facts about the Krishna River are discussed below.
- It is also known by the name of Krishnaveri River.
- The river passes through four states of India – Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
- The river has been named after the Hindu God Krishna. According to the religion, the river is Lord Vishnu’s incarnation.
- It is an important source of water for irrigation.
- The main tributary of the river is known as Tungabhadra which joins it from the right.
- Fluctuations in the flow of the Krishna River are accounted for by monsoon rains. On average, the river discharges 2,213 cubic meters per second.
Yamuna River
The Yamuna River is also known as Jamuna in the local language of the Indians. It is one of the major tributaries of the River Ganges with a length of 1,376 kilometers. The river rises in North India in the Himalayas and takes a course towards the southeast. From there, it reaches Allahabad where it joins the Ganges River as one of its right tributaries.

The significance of the Yamuna River is discussed through the following facts.
- The source of Yamuna is the Yamunotri Glacier.
- The junction between the Yamuna River and Ganges River at Allahabad is religiously significant for Hindus. It is one of the major centers of pilgrimage in the country.
- Taj Mahal at Agra, located at the banks of the rivers is one of India’s major tourist attractions and is famous worldwide.
- The Yamuna River is an important source of irrigation water for the states of Uttar Pradesh and Punjab.
Narmada River
Another of the longest rivers of India, the Narmada River covers a distance of 1,312 kilometers during its course. In fact, it ranks fifth among the longest rivers flowing through the Subcontinent. The river begins its long journey from its source in Madhya Pradesh and reaches its destination at the Gulf Khambhat and joins the Arabian Sea. During its course, the Narmada River discharges 1,447 cubic meters per second on average.

The following informative facts reveal more about the Narmada River.
- The river is also called Rewa by the Indians.
- It is the third longest of the rivers of India which have their course entirely within the boundaries of the country.
- Narmada River is popularly known as the lifeline of the state of Madhya Pradesh owing to its contribution in various ways.
- A natural boundary which separates Northern India and Southern India is formed by the Narmada River.
- The turbulent waters of the river as well as its steep banks make it unsuitable for the purpose of navigation or irrigation.
- According to Hindu belief, the river arose from the body of Shiva god. It is, therefore, an important site of pilgrimage in India.
Brahmaputra River
Also known as Tsangpo-Brahmaputra, the river flows across international borders and runs through India, China as well as Bangladesh. The origin of the river lies in the Himalaya Mountains of Tibet. From there, it carries out a long journey of 2,900 kilometers before flowing into the Indian Ocean through the Bay of Bengal.

Here are some more facts about the Brahmaputra River.
- The name of the river has been derived from the Hindu cast, Brahmin which is considered to be the highest ranking class. It literally means the “male progeny of Brahmin”.
- The Chinese name for the river is Yarlung Zangbo Jiang.
- The basin area of the river is huge and occupies 651,334 square kilometers.
- The Chemayungdung Glacier found on the Himalayas is the main source of the Brahmaputra River.
Indus River
The Indus River is one of the greatest rivers in Asia. It originates from the Kailash range in Tibet, crosses Jammu and Kashmir and enters India. From here, the river flows towards the southwest into Pakistan and finally empties into the Arabian Sea at Karachi. The entire journey of the Indus River takes 3,060 kilometers. Five important rivers flowing through the province of Punjab combine with Indus to form the Indus River System.

More information about the river is discussed below.
- The basin of the river is huge and covers 1,165,000 square kilometers of area.
- The gigantic river discharges 6,600 cubic meters per second.
- According to the Indus Water Treaty mutually signed by India and Pakistan in 1960, the former can utilize only twenty percent of the river’s water.
- Five of its major tributaries giving rise to the Indus River System are Sutlej, Chenab, Jhelum, Ravi and Beas.
- The river has historical importance since civilizations began building cities at its banks back in 3,300 BC. Relics of the famous Indus Valley civilization are still found and preserved.
These were some of the most famous waterways of India. There is a huge number of other large and small rivers flowing through the country which provide a source of water, food and transport to a large population.
India Country - Latest Articles

Religious and Social Customs in India Which are Definite to Follow
Posted By KathleenTraditions and customs have always been given a great deal of significance by people...
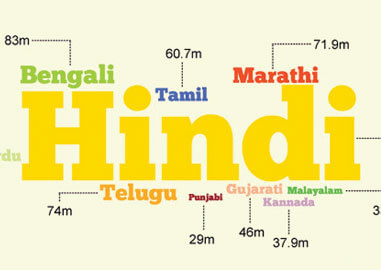
How many Languages are there in India?
Posted By John DoeIndia is known as the largest democracy in the world with a rich history and culture. It is...

Interesting Facts about India-Food, History & Culture
Posted By MariaIndia is one of the most popular countries of the world owing to its historical background...
